State Driven Development
Like many developers, I noticed enums pretty quickly after I started programming in Swift. I had used enums in other programming languages too, but they had never been as exciting to work with and use as enums in Swift. I remember reading this blog post by Casey Liss a few years ago and feeling the exact same excitement enums. Enums in Swift are awesome and fun to use!
The more I use enums in Swift, the more convinced I am that enums are so valuable that they're worth designing software around. We have terms like object oriented programming and protocol oriented programming for describing how we design software around types. How we design software around enums is just as important and useful. I think of designing software around enums as State Driven Development, and that's what I hope to describe here.
But the story of state driven development doesn't start with enums. We need to start with a different programming tool that we're all even more familiar with. It's something that we probably use every day while writing code.
That of course, is BOOL. Specifically BOOLs used as instance variables that represent the state of an object. It's actually a tool that we use ALL the time. We define these properties on objects we create ourselves, often out of convenience, or we set these properties on other objects that we interact with.
var instanceVariable : BoolSo how often do we use BOOLs? We can use a regular expression to search our Xcode project for this pattern to see what all of the examples look like.
// Regex for boolean state
// Match Bool typed vars that aren't computed properties
var.*:.*Bool(\n|.*=.*)
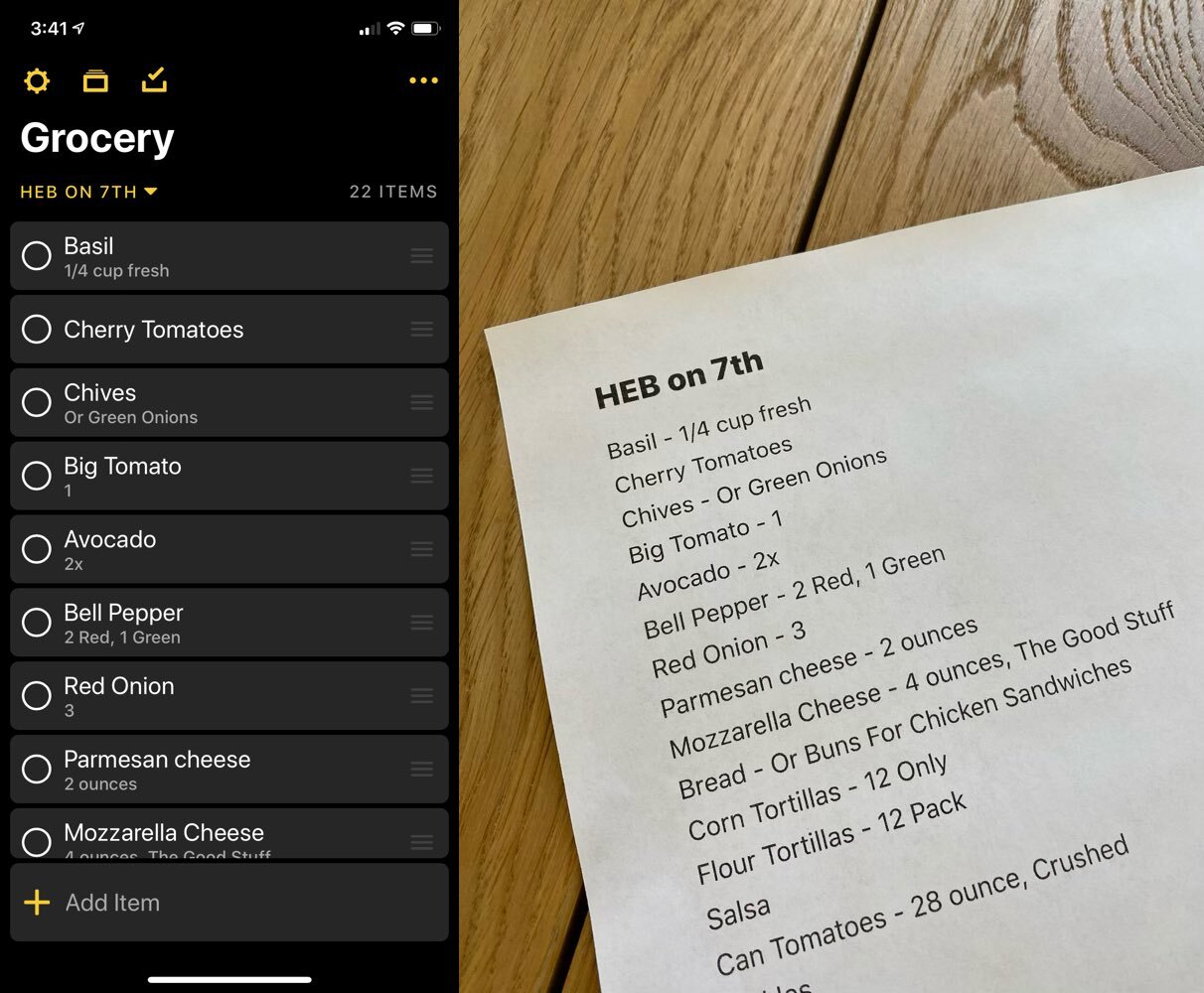
var.*=\s?(true|false)In the project find navigator in Xcode, select Regular Expression from the dropdown and enter the pattern you want to match. If your project is anything like mine you'll probably be pretty surprised at what you find! Below are some of the examples I found in my app Grocery.
var active : Bool
var contentLoaded : Bool
var dataLoaded : Bool
var editing : Bool
var enabled : Bool
var expanded : Bool
var handlingTouches : Bool
var hasTakenUserAction : Bool
var isCompleted : Bool
var isRunning : Bool
var lastTouchedButtonSide : Bool
var lastTouchedRightSide : Bool
var notified : Bool
var previewEnded : Bool
var saved : Bool
var started : Bool
Some of these seem fairly clear in terms of what they mean and when they should be true or false. But the problem with BOOLs is that it's not always clear what they mean. How often do their values change and who is responsible for changing them? How do different BOOLs relate to each other? For example: when one BOOL is true, should another BOOL be false?
Starting a workout
Let's go through an example together. We're working on an app for tracking workouts. The app has one purpose: to allow the user to track a workout. When the user opens the app they can always start a workout. Imagine there's just a giant button that says "start workout". So we write a function that starts a workout when the button is tapped.
func startWorkout() {
// ...
}
This works great, but later on we realize our app can start two workouts if the button is tapped twice. How do we prevent that?
One variable
We add a BOOL to represent whether or not a workout is in progress. Now we can guard against starting a second workout if the first one hasn't finished.
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
func startWorkout() {
guard workoutInProgress == false else {
return
}
workoutInProgress = true
// ...
}
This also works great, for a while. But then we realize there's another requirement missing from this method. If a user hasn't logged into the app yet then we won't be able to save their workout.
Two variables
To prevent that from happening, we add another BOOL to track whether or not the user has logged in. We expect this property to be set to true when the user logs in, and we add another case to our guard statement to make sure it's still true. Now the user has to be logged in to start a workout, and we can only have one workout running at a time.
var hasLoggedIn : Bool = false
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
func startWorkout() {
guard hasLoggedIn && workoutInProgress == false else {
return
}
workoutInProgress = true
// ...
}
This is getting pretty complicated though. First, we need to trust that something will set hasLoggedIn to true. We also need to set workoutInProgress back to false at the end of the workout, or we won't be able to start another workout later. The potential for bugs to creep in has gone up quite a bit just from adding one more variable.
Now we receive another requirement for our start workout method. We want to prevent starting a new workout while we're in the middle of saving the prior workout so we add a new variable to track if we are currently saving a workout.
The tangled web of state
This is where the web of state starts to get very tangled. First we set workoutInProgress equal to false since we've stopped tracking the workout, but saving the workout is an asynchronous task, so we set the savingWorkout variable to true when we start saving, and back to false when we finish saving.
var hasLoggedIn : Bool = false
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
var savingWorkout : Bool = false
func stopWorkout() {
workoutInProgress = false
savingWorkout = true
saveWorkout { (success) in
self.savingWorkout = false
}
}
Back in our start workout method, we need to add a third case to our guard. The user still has to be logged in, and they can't start a workout if there is a workout still in progress or being saved.
var hasLoggedIn : Bool = false
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
var savingWorkout : Bool = false
func startWorkout() {
guard hasLoggedIn && workoutInProgress == false && !savingWorkout else {
return
}
workoutInProgress = true
// ...
}
But that's turning into a really long guard statement. There's a lot that we need to remember to do as programmers to make sure that all of these state variables operate the way that this function expects them to.
Valid and invalid states
So here's what's crazy about this. We have 3 BOOL values, but by combining them together we can represent 8 completely distinct states, even though only 4 of them are actually valid states for our application to be in.
var hasLoggedIn : Bool
var workoutInProgress : Bool
var savingWorkout : BoolThese are the four combinations of values that are actually valid. They follow the user's expected path through the application. The user logs in, starts a workout, and saves the workout.
- User Not Logged In, No Workout, Not Saving
- User Logged In, No Workout, Not Saving
- User Logged In, Workout In Progress, Workout Not Saving
- User Logged In, No Workout, Workout Is Saving
But with BOOLs we can represent combinations of values that shouldn't be possible. These four combinations represent potential bugs. They are states we could accidentally find ourselves in if we fail to update our BOOLs correctly. Something like the user not being logged in, but still having both a workout in progress and another workout being saved.
- User Not Logged In, Workout In Progress, Not Saving
- User Not Logged In, Workout In Progress, Workout Is Saving
- User Not Logged In, No Workout, Workout Is Saving
- User Logged In, Workout In Progress, Workout Is Saving
This is the perfect case for creating an enum. We have four valid states that we've identified, and we know that our object should only ever be in one of these states. We need to construct an enum that shows exactly which of those 4 states our object is in.
These are our four valid states:
- Hasn't logged into the app yet
- In the middle of a workout
- Saving the last workout
- Idle
And here's what they look like as an enum:
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
case notLoggedIn
case workoutInProgress
case savingLastWorkout
case idle
}
By using an enum instead of multiple BOOL values we've actually made the invalid states impossible to represent in code. That's going to make an entire class of bugs impossible to write, because we can't cause our app to be in a state that can't be represented.
But our job isn't done yet. Even though we've created an enum to accurately describe the state of our object, we still have to update our code to ask specific questions using the enum we’ve defined.
Asking specific questions
The question we're trying to ask in our guard statement is: "Can I start a workout? 🤔" But that's not what the code here is asking yet. The question it's asking is actually pretty vague. These three variables are describing the state of the object. They're intended to answer questions like whether or not the user has logged in. They weren't designed to answer questions about starting workouts.
var hasLoggedIn : Bool = false
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
var savingWorkout : Bool = false
func startWorkout() {
guard hasLoggedIn && workoutInProgress == false && !savingWorkout else {
return
}
workoutInProgress = true
// ...
}
We can improve the code by referencing our lifecycle enum. The idle case happens to be the only case where we can start a workout, so technically this code will work. But we're still comparing two values to see if they’re equal instead of asking a specific question about starting a workout.
var lifecycle : WorkoutApplicationLifecycle = .notLoggedIn
func startWorkout() {
guard lifecycle == .idle else {
return
}
workoutInProgress = .workoutInProgress
// ...
}Extending enums with variables!
Fortunately, Swift gives us a great way to ask more specific questions and implement custom behavior with our enums. We can extend our lifecycle enum with a variable that answers the question: can we start a workout? We know that the app should only start a workout in the idle case, so we return true there and return false for the other cases.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
case notLoggedIn
case workoutInProgress
case savingLastWorkout
case idle
var canStartWorkout : Bool {
get {
switch self {
case .notLoggedIn, .workoutInProgress, .savingLastWorkout:
return false
case .idle:
return true
}
}
}
}
Here's what using our new canStartWorkout extension looks like in the guard statement.
var lifecycle : WorkoutApplicationLifecycle = .notLoggedIn
func startWorkout() {
guard lifecycle.canStartWorkout else {
return
}
lifecycle = .workoutInProgress
// ...
}
Our stopWorkout method also sets our lifecycle correctly to indicate when the app is saving a workout and when the app is back to being idle.
var lifecycle : WorkoutApplicationLifecycle = .notLoggedIn
func stopWorkout() {
lifecycle = .savingLastWorkout
saveWorkout { (success) in
self.lifecycle = .idle
}
}This way, our enum cases can cleanly represent state, and our enum extensions can clearly describe the questions that our enum is able to help answer.
Avoiding direct case comparison
Here's another example of why it's best to avoid direct case comparison with enums and implement extensions to answer specific questions. Consider a collection of possible activity types. We have an ActivityType enum that enumerates running, walking, and yoga activities.
enum ActivityType {
case running
case walking
case yoga
}
There are plenty of questions that the activity type can help us answer. One of them is whether or not to start the GPS system. Let's say that we only want to use GPS for running workouts. We check if our activity type is equal to running, and turn GPS on or off.
if activityType == .running {
gpsProvider.start()
}
if activityType == .running {
gpsProvider.stop()
}
Eventually we decide to use GPS for walking workouts too, so we update our first if statement to support walking. But we forgot to update the second if statement, and now our app has a bug because we won't turn GPS off when the user stops walking.
if activityType == .running ||
activityType == .walking {
gpsProvider.start()
}
if activityType == .running {
gpsProvider.stop()
}
When we check for equality between two enum cases, we lose the opportunity to create a single source of truth for state driven behaviors. Let's say we wanted a hiking activity to support GPS as well. Wouldn't it be nice to have one place to make that change?
The question we're trying to ask is whether or not our activity type supports GPS. We can extend our enum with a variable to answer that question, using its own cases to customize the behavior. Whenever we're ready to add hiking, we'll just have one change to support GPS.
enum ActivityType {
case running
case walking
case yoga
var supportsGPS : Bool {
switch self {
case .running, .walking:
return true
case .yoga:
return false
}
}
}
if activityType.supportsGPS {
gpsProvider.start()
}
It's important to consider how enum extensions can help us describe custom behavior and answer specific questions about the state of our objects. Once we start thinking about specific questions, we can start extending our enums to help provide specific answers.
There are lots of questions we might want to ask our enums that aren't inherently answered by the names of specific cases. Nothing about the name of an activity type describes if it should support GPS. Adding an extension for that specific question is how we describe that custom behavior.
The best rule of thumb here is that any time that a program needs to use state to answer a question, there should be enum extension to help answer it.
Extend enums with functions!
We can also extend enums with functions so that we can take different actions depending on the state of the object.
Back in our original example, we've defined an action taken method on the enum that accepts a reference to the view controller. The enum can then take advantage of the view controller’s public API without having to know anything about its internal structure. The view controller exposes start, stop, and save methods that our enum can use.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
// ...
func actionTaken(from viewController : WorkoutViewController) {
switch self {
case .notLoggedIn:
viewController.login()
case .workoutInProgress:
viewController.stopWorkout()
viewController.saveWorkout()
case .savingLastWorkout:
break
case .idle:
viewController.startWorkout()
}
}
}
What's nice about this is that the logic for what to do when the button is pressed is entirely encapsulated in the thing that describes the possible states of the button. All we have to do when we want to change behavior is change the options described by that enum case.
It may seem strange to literally pass something like a view controller to a function on an enum. Should the enum actually have access to something that substantial? I like this pattern for a few reasons. First, the dependency is explicitly created because the view controller is passed as an argument to the function, rather than implicitly accessed as a property. Second, the enum can't hold onto the view controller, so it can only use it's API inside of this specific function. It ends up being a safer way to reuse code than many other types of less-specific dependencies.
Our view controller benefits from this encapsulation too with a very clean IBAction implementation.
@IBAction func didTapActionButton() {
lifecycle.actionTaken(from: self)
}Describing custom behavior
We can keep extending our enum to describe more behaviors. We can ask the state for the answers to questions like what the title of an action button is, or what background color to use.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
case notLoggedIn
case workoutInProgress
case savingLastWorkout
case idle
var canStartWorkout : Bool
var actionTitle : String
var backgroundColor : UIColor
var barButtonItems : [UIBarButtonItem]
}
In this example, the enum knows what the state of our lifecycle is, so it can return the correct action title for each state.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
var actionTitle : String {
get {
switch self {
case .notLoggedIn:
return "Sign In"
case .workoutInProgress:
return "End Workout"
case .idle:
return "Start Workout"
default:
return ""
}
}
}
}Note: It's important to be careful using default switch statements, because the compiler won't warn us when new cases are added to our enum. I typically avoid using it unless absolutely necessary, even when only one case needs to return a different value.
We can also return different background colors for different states.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
var backgroundColor : UIColor {
get {
switch self {
case .notLoggedIn:
return UIColor.blue
case .workoutInProgress: fallthrough
case .savingLastWorkout:
return UIColor.red
case .idle:
return UIColor.green
}
}
}
}Note: Some switch statements benefit from using the fallthrough syntax to return the same values for multiple cases. Fallthrough requires the explicit use of the fallthrough keyword as opposed to implicit implementations in other languages like Objective-C. So we have to opt-in to using fallthrough, but I like this option and I've started using it more often.
The temptation of BOOL
Every time we add a state, it's tempting to use a BOOL instead of an enum. They're easy to create and simple to use.
var workoutInProgress : Bool = false
func startWorkout() {
guard workoutInProgress == false else {
return
}
// ...
}
But even from just the first BOOL we defined, it would have been better to use an enum. The purpose of the workoutInProgress state variable is different from the guard statement's question of whether or not it can start a workout. Having the enum gives us an obvious extension point when the states and behavior of the object need to change in the future.
As I've been exploring State Driven Development, I've been trying to always describe state with an enum instead of a BOOL. But sometimes I do still use a BOOL just to see how it goes.
var trap : BoolEvery time I've gone ahead with creating a BOOL I've gone back and replaced it with an enum. Enums are just a better tool for being specific about state, and being able to answer a broad range of questions that depend on state. It's become a foundational part of how I like to write software.
When we set the value of an enum, we're telling the object what state it's in. Our lifecycle enum is describing the states the object can be in. It's telling us that we're in the workout recording state, or the saving a workout state, or the not logged in state, or the idle state.
Any time that a program enters a state, there should be an enum defined with a case to describe it.
Adding new states
The real ah-ha moment for State Driven Development comes when we need to add a new case to our enum. We need to add a new state to support restoring a workout.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
case restoringWorkout
}
After adding the new case, our switch statements prompt us to implement it in all of our extension variables and functions.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
var backgroundColor : UIColor {
get {
switch self {
case .notLoggedIn:
return UIColor.blue
case .workoutInProgress: fallthrough
case .savingLastWorkout:
return UIColor.red
case .idle:
return UIColor.green
case .restoringWorkout:
// return ?
}
}
}
}
This turns our enum extensions into the public API for extending the behavior of our object! As long as we avoid direct case comparisons and the default switch statement, the compiler will tell us exactly what we need to change to support the new case. That allows us to answer each of the specific questions below:
- Can start workout? -
false - Action title? -
default - Background color? -
UIColor.red - Action taken? -
break
This ends up being a much faster and safer way to extend behavior to support new states. Since we have a single source of truth for making decisions that involve state, we don't need to remember where various BOOLs or enum cases were used throughout the code base and check to see if they require updates to handle the new state.
Associated values
Now that we've covered the basics of State Driven Development, I want to focus on a few features of enums in Swift and how they make State Driven Development even better. Associated Values are my favorite Swift enum feature! An associated value is basically a tuple that we can add to any enum case. We can access the values stored in that case's tuple whenever we need to.
Here's what the syntax looks like for specifying that an enum case has an associated value. The enum case is workoutInProgress, and current is the parameter name of a Workout object.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
// ...
case workoutInProgress(current : Workout)
}
When we want to get the associated value out of an enum case we can do it with Swift's pattern matching syntax. Since the value is a constant we have to use let to tell swift to treat it as a constant.
if case .workoutInProgress(let workout) = lifecycle {
// ...
}
Slightly confusingly, all of these are actually valid syntax for obtaining an associated value from an enum case. The call-site name can be used or ignored, and let can be after the case or inside the parentheses. When we use let after case then it applies to all of the associated values within the tuple, which is actually pretty handy if you have multiple associated values for one enum case.
if case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout) = lifecycle { }
if case let .workoutInProgress(workout) = lifecycle { }
if case .workoutInProgress(let workout) = lifecycle { }
The associated value can also be ignored if it isn't needed.
if case .workoutInProgress = lifecycle { }
These are the same examples for building switch statements, all of which are valid syntax as well.
switch self {
case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout):
case let .workoutInProgress(workout):
case .workoutInProgress(let workout):
case .workoutInProgress:
}
This is the syntax that I prefer using. The compiler autocompletes the call-site name "current" for us, so all we have to do is hit enter and type a variable name. I like using let after case so that it applies to all of the associated values.
if case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout) = lifecycle { }
switch self {
case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout):
}
Here's what setting an associated value looks like. Back on our start workout method, we create the new workout object and pass it along when we set our lifecycle to the workout in progress state.
var lifecycle : WorkoutApplicationLifecycle = .notLoggedIn
func startWorkout() {
guard lifecycle.canStartWorkout else {
return
}
var newWorkout : Workout = Workout()
// ...
lifecycle = .workoutInProgress(current: newWorkout)
}
We can use the associated value to help answer more types of questions by expanding the scope of our enum cases. Here we're using it to return a different title based on our current workout's activity type.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
// ...
case workoutInProgress(current: Workout)
var navigationTitle : String {
switch self {
case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout):
return workout.type.activityName
}
}
}Highly relevant values
Associated values are highly relevant to the states of our objects. It makes a lot of sense to have the workout property live within the workoutInProgress case because that's the only state where our object can have an active workout.
We can pass the in progress workout's associated value to our save workout method to specify the workout that needs to be saved.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
// ...
case workoutInProgress(current: Workout)
func actionTaken(from viewController : WorkoutViewController) {
switch self {
case let .workoutInProgress(current: workout):
viewController.stopWorkout()
viewController.saveWorkout(current: workout)
}
}
}
Result is another example where having highly relevant values is useful.
@frozen enum Result<Success, Failure> where Failure : Error {
case success(Success)
case failure(Failure)
}
It makes sense that the Result enum only includes Error as an associated value on the failure case because the error is only relevant when there's been a failure. When we need to handle the failure we have the error available to use within that context. Otherwise we don’t need to worry about it.
Providing useful context
Enum cases with associated values can help provide useful context. In this example, our table view cell has defined a protocol for the types of content it can display. Most of the content properties are optional though, because the cell can support showing an image without text, or text without images.
protocol TableViewCellContent {
var titleText : String?
var descriptionText : String?
var image : UIImage?
var accessoryType : UITableViewCellAccessoryType
}
// Supported Configuration Options
* Simple cell with one line of text
* Detailed cell with two lines of text
* Image Cell
* Accessory Image Cell
We can create a cell configuration enum with associated values to provide the context for when specific cell content should be used. And since enums can conform to protocols, our configuration enum will implement property getters for all of the variables defined by the cell content protocol and return the associated values specified by each configuration.
protocol TableViewCellContent {
var titleText : String?
var descriptionText : String?
var image : UIImage?
var accessoryType : UITableViewCellAccessoryType
}
enum CellConfiguration : TableViewCellContent {
case simpleCell(title : String)
case detailedCell(title : String, description : String)
case imageCell(image : UIImage)
case accessoryCell(title : String,
image : UIImage,
accessory : UITableViewCellAccessoryType)
}
With our cell configuration enum in place, we can define mapping functions on our model objects to return the cell configuration best suited for the data they need to show.
extension Workout {
var cellConfiguration : CellConfiguration {
return .detailedCell(title: workoutTitle,
description: activityType.description)
}
}
extension User {
var cellConfiguration: CellConfiguration {
return .imageCell(image: profileImage)
}
}
What's nice about this pattern is that it keeps details of the data models outside of the cell configurations. The part of our app that chooses how to represent a model object is basically reading a menu, and choosing what to order from of it.
"I'll have a detailed cell with a workout title and an activity type description".
Our cellForRowAtIndexPath implementation is a lot simpler too because we don't have to worry about performing any configuration here. When we dequeue our cell we just get our model object for that row, and setup the cell with the enum case for that type of model object.
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView,
cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell
(withReuseIdentifier: reuseIdentifier,
for: indexPath) as! CustomTableViewCell
let workout = workouts[indexPath.row]
cell.setup(with: workout.cellConfiguration)
return cell
}
And because our cell defined a protocol for its content, the cell doesn't need to know anything about the enum that implemented the protocol. It's just using the content that it was provided with.
class CustomTableViewCell : UITableViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var titleLabel : UILabel?
@IBOutlet weak var descriptionLabel : UILabel?
@IBOutlet weak var imageView : UIImageView?
func setup(with content : TableViewCellContent) {
titleLabel?.text = content.titleText
descriptionLabel?.text = content.descriptionText
imageView?.image = content.image
accessoryType = content.accessoryType
}
}Single source of truth
Enums can also be the single source of truth for complex objects like view controllers.
There are usually several "modes" that a view controller can be in. The modes might be designed around features like viewing or editing a document, or recording or saving a workout.
A lot of things can change based on the mode. The navigation bar title and bar buttons may be different. There might be an overlay view that's hidden or visible. There might be an activity indicator that's started or stopped. Reasoning about all of these appearance customizations can be a big challenge without a single source of truth that describes what they all do in each possible state.
protocol ViewControllerAppearance {
var title : String
var leftBarButtonItems : [UIBarButtonItem]
var rightBarButtonItems : [UIBarButtonItem]
var overlayAlpha : CGFloat
var activityIndicatorActive : Bool
}
enum ViewControllerState : ViewControllerAppearance {
case .editing(Workout)
case .saving(Workout)
case .viewing(Workout)
}
I fixed an issue recently where I was showing the wrong navigation bar button items for the state that the view controller was in. The screen was showing a cancel button instead of a close button because the navigation items where changing separately from where my view controller's state was being changed.
A great way to fix these types of issues is to implement appearance customizations as a function of state.
Appearance as a function of state
We can define a setupView function and pass in the state that we're transitioning to. The function can perform any necessary setup based on the requirements specified by our state enum.
func setupView(for state: ViewControllerState) {
navigationItem.title = state.title
navigationItem.leftBarButtonItems = state.leftBarButtonItems
navigationItem.rightBarButtonItems = state.rightBarButtonItems
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.35) {
self.overlayView.alpha = state.overlayAlpha
}
if state.activityIndicatorActive {
activityIndicator.startAnimating()
} else {
activityIndicator.stopAnimating()
}
}Behavior as a function of state
Other behavior is likely to change based on our view controller's state too. We might have different table view cell selection behavior for editing a document versus viewing it. We might also have a completely different data source to show in each state.
protocol ViewControllerBehavior {
func didSelectCell(at indexPath: IndexPath)
func highlightCell(at indexPath: IndexPath)
func handleDragOnCell(at indexPath: IndexPath)
func numberOfRows(in section: Int) -> Int
var numberOfSections: Int
var supportsDragAndDropInteraction: Bool
}
extension ViewControllerState : ViewControllerBehavior {}
At some level, everything about a screen depends on the state it is in. By moving all of this logic into an enum, especially a single enum that describes all of the possible states that the screen needs to represent, we greatly simplify our view controller implementation and keep all of our complex logic contextual to where the states are defined.
Swift special features: CaseIterable
There are of course several other features that make using enums in Swift even easier. It's entirely possible to write an entire app without using some of these features, but when you do need them it really is nice to have them.
One of these features is CaseIterable. If we need to iterate through all of an enum’s cases we can conform to the CaseIterable protocol. When we conform to CaseIterable, Swift automatically implements an allCases property for us and keeps it updated when we add or remove cases.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle : CaseIterable {
case notLoggedIn
case workoutInProgress
case savingLastWorkout
case idle
}
WorkoutApplicationLifecycle.allCases
[notLoggedIn, workoutInProgress, savingLastWorkout, idle]Note: While it is possible to conform to CaseIterable inside of an extension, we do need to conform to the protocol in the same file that our enum is defined in or it won't work.
We can also provide a custom implementation of allCases if we want to, which is important for enums that use associated values. Swift can't know all of the possible associated values, so it will complain unless we provide an implementation.
enum WorkoutApplicationLifecycle {
case notLoggedIn
case workoutInProgress(current : Workout)
case savingLastWorkout
case idle
}
extension WorkoutApplicationLifecycle : CaseIterable {
static var allCases: [WorkoutApplicationLifecycle] {
return [.notLoggedIn, .savingLastWorkout, .idle]
+ WorkoutActivityType.allCases.map(.workoutInProgress)
}
}
The downside, of course, is we do have to remember to keep this updated if our cases change.
Swift special features: RawRepresentable
Enums in Swift can also have raw values. Traditionally, most enums use Ints as their raw values, but we can use Strings too. This is really useful for defining things like keys that we want to reuse in multiple places.
enum DefaultKeys : String {
case loggedInUserId
case selectedActivityType
}
print(DefaultKeys.selectedActivityType.rawValue)
selectedActivityType
Swift can define the raw value as the name of each case automatically, or we can provide our own raw value for each case. Here we're defining a specific string for the selected activity type case, and that's the string we get back when we access the raw value.
enum DefaultKeys : String {
case loggedInUserId
case selectedActivityType = "SelectedActivityTypeDefaultKey"
}
print(DefaultKeys.selectedActivityType.rawValue)
SelectedActivityTypeDefaultKey
Support for String and Int raw values is built into Swift, but because Enums can conform to protocols we can actually make an enum work with any raw value by conforming to the RawRepresentable protocol. Here we have an Application Theme enum that defines different color schemes. The enum is defining the options, but there is a separate struct that is actually defining the values that our interface needs to configure itself.
enum ApplicationTheme {
case defaultLight
case darkMode
case blueberry
case eggplant
case mustard
case broccoli
}
struct Theme : Equatable {
let name : String
let background : UIColor
let cell : UIColor
let tint : UIColor
let foreground : UIColor
let statusBar : UIStatusBarStyle
}
How can we return the correct Theme struct for each ApplicationTheme enum case? One option is to define a custom raw value on the ApplicationTheme enum. We conform to RawRepresentable on our ApplicationTheme enum and make the Theme struct its raw value. Once we're done we'll have direct access to the theme struct right from the enum case.
enum ApplicationTheme : RawRepresentable {
typealias RawValue = Theme
init?(rawValue: Theme) {
// ...
}
var rawValue: Theme {
// ...
}
}
print(ApplicationTheme.broccoli.rawValue.name)
Brocolli
Enums with custom raw values don't support associated values, so we do have to pick and choose which approach makes the most sense for our use case. We could have decided to use associated values to solve this problem by initializing every case with a Theme struct.
enum ApplicationTheme {
case defaultLight(theme : Theme)
case darkMode(theme : Theme)
case blueberry(theme : Theme)
case eggplant(theme : Theme)
case mustard(theme : Theme)
case broccoli(theme : Theme)
}
The problem with using associated values in this example is that we need to know which Theme struct to pass in to create each case. That's hard to define, since the enum case can be initialized with any theme struct and not just the specific one intended for that case. This makes it almost impossible to enforce correctness which in-turn makes the enum harder to use.
Since there are tradeoffs between associated values and custom raw values, I recommend looking at associated values first. If most or all of the associated values are duplicates, then it's a good indication that a custom raw value makes more sense for the use case.
Another benefit of using a custom raw value is that it makes supporting CaseIterable easier, since we don't have any associated values.
enum ApplicationTheme : CaseIterable {
case defaultLight
case darkMode
case blueberry
case eggplant
case mustard
case broccoli
}
ApplicationTheme.allCases
[.defaultLight, .darkMode, .blueberry, .eggplant, .mustard, .broccoli]
The default implementation of CaseIterable works perfectly for our ApplicationTheme enum and gives us back an ordered list of all our theme options from one variable that the compiler will maintain for us.
🎉 Confetti Moments 🎊
I wanted to end this post with something fun by sharing one of my favorite real-world enums that I've created.
During a recent hackathon project I added easter egg confetti effects to the MapMyRun and MyFitnessPal apps. I used an enum to define the type of confetti we could show, including custom colors, images, or even emoji.
public enum ConfettiMoment {
// Color Confetti
case confettiMMF
case confettiMFP
case confetti🏳️🌈
// Emoji Confetti
case 🌮
// Custom Confetti
case customColors(colors : [UIColor], name : String)
case customImages(images : [UIImage], name : String)
func effectScene() -> SKScene
}We have some colors and emoji confetti moments pre-specified, and two additional cases for specifying custom colors and images. Each case just needs to return an effect scene for creating the confetti. The confetti can appear when someone completes their diary, congratulates someone on a great workout, or mentions tacos in a workout post on Taco Tuesday.
Try it!
I've loved hearing from other developers who, after hearing about State Driven Development, have gone back to try it in their projects. I've talked to many people who have used enums as a way to simplify complex states within their applications and be more specific about answering questions as a function of state.
If you want to try State Driven Development in your project, try creating an enum to describe state instead of a BOOL. I like this approach to getting started because creating an enum instead of a BOOL is easy to remember. Once you've done that, try defining an extension to answer a question as a function of state.
I've adapted this post from two different conference talks where I've spoken about State Driven Development and enums in Swift. I loved putting those talks together and sharing them, which is what motivated me to create a written account of this content and share it here. If you want to see the original talks check out the links below.
- 360iDev 2018 - Enumerating all of the reasons why enums are AWESOME!
- UIKonf 2020 - State Driven Development - The Beauty of Enums in Swift
Additional resources
If you want keep exploring enums, there are a few specific blog posts and articles that I've found very helpful in thinking about enums in my own work. These are a few examples on enum driven table views, and an awesome series on pattern matching.
- https://www.swiftbysundell.com/posts/the-power-of-result-types-in-swift
- https://oleb.net/blog/2018/06/enumerating-enum-cases/
- https://www.raywenderlich.com/5542-enum-driven-tableview-development
- https://alisoftware.github.io/swift/pattern-matching/2016/03/27/pattern-matching-1/
These are a few posts that serve as helpful references on Swift enum features.
- https://oleb.net/blog/2018/06/enumerating-enum-cases/
- https://www.hackingwithswift.com/read/0/14/enumerations
- https://www.hackingwithswift.com/articles/161/how-to-use-result-in-swift
- https://www.swiftbysundell.com/posts/the-power-of-result-types-in-swift
And these examples focus on strategies that improve code quality in Swift and have some awesome references for how enums can help you do that.
- https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swift/maintaining_state_in_your_apps
- https://khanlou.com/2018/04/enums-and-optionals/
- https://www.swiftbysundell.com/posts/writing-self-documenting-swift-code
- https://www.swiftbysundell.com/posts/code-encapsulation-in-swift
- https://ericasadun.com/2015/05/26/swift-the-hall-of-the-dwarven-enumeration-king/#more-1529
- https://github.com/pointfreeco/swift-enum-properties
- https://www.caseyliss.com/2016/2/27/swift-enums